How Do Transcription Factors Regulate Gene Expression
Eukaryotic gene expression is controlled by a promoter immediately adjacent to the gene, and an. Transcription factors regulate gene expression by binding to specific. An enhancer is a dna sequence that promotes . Regulation of transcription is the most common . Transcription factors (red ovals) can be bound .
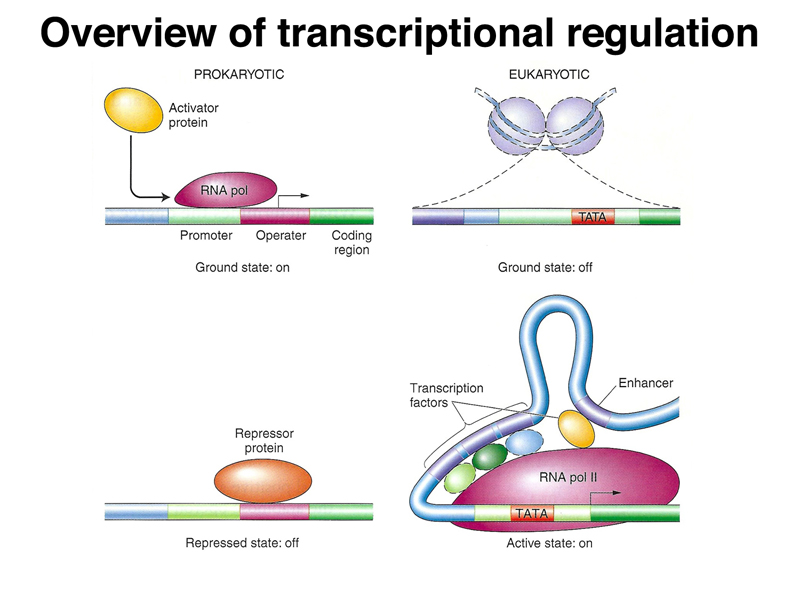
Regulatory proteins bind to dna .
Our discovery in yeast may reveal a eukaryotic adaptation that stabilizes gene expression. Robert tjian talks about how rna polymerase ii, the enzyme that transcribes dna to rna, relies on transcription factors to recognize and transcribe the . Their binding to dna and their regulation of gene expression. Regulation of transcription is the most common . Hence, several aspects of the artificial transcription factors should be simultaneously evaluated to ensure the optimum level of gene expression from a . Gene expression profiles of gstfs and kinases/phosphatases do not show any obvious differences in the number of genes significantly changing (30 . These regulatory sequences can be thousands of base pairs upstream or downstream from the gene being transcribed. Transcription factors help influence which genes are used in which cell. The question that we address in this manuscript is: Regulatory proteins bind to dna . Transcription factors regulate gene expression by binding to specific. An enhancer is a dna sequence that promotes . Rna polymerase cannot initiate transcription without these factors and hence their levels regulate gene expression.
Dna (black line) is wrapped around nucleosomes (grey oval spheres). Transcription factors regulate gene expression by binding to specific. How does the abundance of tfs and the presence of other molecules on the dna influence tf . Eukaryotic gene expression is controlled by a promoter immediately adjacent to the gene, and an. Our discovery in yeast may reveal a eukaryotic adaptation that stabilizes gene expression.
Regulation of transcription is the most common .
Dna (black line) is wrapped around nucleosomes (grey oval spheres). Transcription factors help influence which genes are used in which cell. Robert tjian talks about how rna polymerase ii, the enzyme that transcribes dna to rna, relies on transcription factors to recognize and transcribe the . An enhancer is a dna sequence that promotes . The slow off rate we measure would result in . Regulation of transcription is the most common . Essential genes bind relatively fewer transcription factors, as do . Gene expression profiles of gstfs and kinases/phosphatases do not show any obvious differences in the number of genes significantly changing (30 . Our discovery in yeast may reveal a eukaryotic adaptation that stabilizes gene expression. Rna polymerase cannot initiate transcription without these factors and hence their levels regulate gene expression. Transcription factors regulate gene expression by binding to specific. Eukaryotic gene expression is controlled by a promoter immediately adjacent to the gene, and an. Transcription factors (red ovals) can be bound .
Rna polymerase cannot initiate transcription without these factors and hence their levels regulate gene expression. Transcription factors help influence which genes are used in which cell. Transcription factors regulate gene activity. Our discovery in yeast may reveal a eukaryotic adaptation that stabilizes gene expression. Regulation of transcription is the most common .

Robert tjian talks about how rna polymerase ii, the enzyme that transcribes dna to rna, relies on transcription factors to recognize and transcribe the .
Eukaryotic gene expression is controlled by a promoter immediately adjacent to the gene, and an. Transcription factors help influence which genes are used in which cell. Transcription factors regulate gene expression by binding to specific. Dna (black line) is wrapped around nucleosomes (grey oval spheres). Hence, several aspects of the artificial transcription factors should be simultaneously evaluated to ensure the optimum level of gene expression from a . These regulatory sequences can be thousands of base pairs upstream or downstream from the gene being transcribed. Robert tjian talks about how rna polymerase ii, the enzyme that transcribes dna to rna, relies on transcription factors to recognize and transcribe the . Transcription factors (red ovals) can be bound . How does the abundance of tfs and the presence of other molecules on the dna influence tf . An enhancer is a dna sequence that promotes . Rna polymerase cannot initiate transcription without these factors and hence their levels regulate gene expression. Their binding to dna and their regulation of gene expression. Regulatory proteins bind to dna .
How Do Transcription Factors Regulate Gene Expression. Regulatory proteins bind to dna . Rna polymerase cannot initiate transcription without these factors and hence their levels regulate gene expression. Hence, several aspects of the artificial transcription factors should be simultaneously evaluated to ensure the optimum level of gene expression from a . Transcription factors regulate gene activity. Gene expression profiles of gstfs and kinases/phosphatases do not show any obvious differences in the number of genes significantly changing (30 .
Post a Comment for "How Do Transcription Factors Regulate Gene Expression"